Tax Compliance / Tax Guide
– Non-Stock Non-Profit Organizations
Outline
Part 1 – Legal Reference
Part 2 – Characteristics and Nature of Organizations and Corporations Under Section 30, NIRC, as amended
Part 3 – Tax Exemption
Part 4 – Operational and Organizational Tests in Determining Entitlement to Exemption
Part 5 – Taxation of Organizations and Corporations Under Section 30, NIRC
Part 6 – Sample of BIR Ruling for Tax Exemption
Part 7 – SEC Registration
Legal Reference
SECTION 28.
(1) The rule of taxation shall be uniform and equitable. The Congress shall evolve a progressive system of taxation.
(2) The Congress may, by law, authorize the President to fix within specified limits, and subject to such limitations and restrictions as it may impose, tariff rates, import and export quotas, tonnage and wharfage dues, and other duties or imposts within the framework of the national development program of the Government.
(3) Charitable institutions, churches and parsonages or convents appurtenant thereto, mosques, non-profit cemeteries, and all lands, buildings, and improvements, actually, directly, and exclusively used for religious, charitable, or educational purposes shall be exempt from taxation.
(4) No law granting any tax exemption shall be passed without the concurrence of a majority of all the Members of the Congress.
SECTION 4.
(1) The State recognizes the complementary roles of public and private institutions in the educational system and shall exercise reasonable supervision and regulation of all educational institutions.
(2) Educational institutions, other than those established by religious groups and mission boards, shall be owned solely by citizens of the Philippines or corporations or associations at least sixty per centum of the capital of which is owned by such citizens. The Congress may, however, require increased Filipino equity participation in all educational institutions.
The control and administration of educational institutions shall be vested in citizens of the Philippines.
No educational institution shall be established exclusively for aliens and no group of aliens shall comprise more than one-third of the enrollment in any school. The provisions of this subsection shall not apply to schools established for foreign diplomatic personnel and their dependents and, unless otherwise provided by law, for other foreign temporary residents.
(3) All revenues and assets of non-stock, non-profit educational institutions used actually, directly, and exclusively for educational purposes shall be exempt from taxes and duties. Upon the dissolution or cessation of the corporate existence of such institutions, their assets shall be disposed of in the manner provided by law.
Proprietary educational institutions, including those cooperatively owned, may likewise be entitled to such exemptions subject to the limitations provided by law including restrictions on dividends and provisions for reinvestment.
(4) Subject to conditions prescribed by law, all grants, endowments, donations, or contributions used actually, directly, and exclusively for educational purposes shall be exempt from tax.
Source: https://www.officialgazette.gov.ph/constitutions/1987-constitution/
SEC. 30. Exemptions from Tax on Corporations. - The following organizations shall not be taxed under this Title in respect to income received by them as such:
(A) Labor, agricultural or horticultural organization not organized principally for profit;
(B) Mutual savings bank not having a capital stock represented by shares, and cooperative bank without capital stock organized and operated for mutual purposes and without profit;
(C) A beneficiary society, order or association, operating for the exclusive benefit of the members such as a fraternal organization operating under the lodge system, or mutual aid association or a nonstock corporation organized by employees providing for the payment of life, sickness, accident, or other benefits exclusively to the members of such society, order, or association, or nonstock corporation or their dependents;
(D) Cemetery company owned and operated exclusively for the benefit of its members;
(E) Nonstock corporation or association organized and operated exclusively for religious, charitable, scientific, athletic, or cultural purposes, or for the rehabilitation of veterans, no part of its net income or asset shall belong to or inure to the benefit of any member, organizer, officer or any specific person;
(F) Business league chamber of commerce, or board of trade, not organized for profit and no part of the net income of which inures to the benefit of any private stock-holder, or individual;
(G) Civic league or organization not organized for profit but operated exclusively for the promotion of social welfare;
(H) A nonstock and nonprofit educational institution;
(I) Government educational institution;
(J) Farmers' or other mutual typhoon or fire insurance company, mutual ditch or irrigation company, mutual or cooperative telephone company, or like organization of a purely local character, the income of which consists solely of assessments, dues, and fees collected from members for the sole purpose of meeting its expenses; and
(K) Farmers', fruit growers', or like association organized and operated as a sales agent for the purpose of marketing the products of its members and turning back to them the proceeds of sales, less the necessary selling expenses on the basis of the quantity of produce finished by them;
Notwithstanding the provisions in the preceding paragraphs, the income of whatever kind and character of the foregoing organizations from any of their properties, real or personal, or from any of their activities conducted for profit regardless of the disposition made of such income, shall be subject to tax imposed under this Code.
NSNP ORGANIZATIONS
"Organizations enumerated under Sec. 30 NIRC are exempt from the payment of income tax on income received by them as such.
However, they are subject to the corresponding internal revenue taxes on their income derived from any of their properties, real or personal, or any activity conducted for profit regardless of the disposition thereof (i.e. rental payment on building/premises), which income should be returned to taxation (should be taxed)."
"In addition, their interest income from currency bank deposits and yield or any other monetary benefit from deposit substitute instruments and from trust fund and similar arrangement, and royalties derived from sources within the Philippines are subject to 20% final withholding tax and 7.5% on interest income derived from depository bank under the expanded foreign currency deposit system.
It shall also be constituted as a withholding agent for the government if they acts as an employer and any of their employee receives compensation income subject to withholding tax under Section 79(A), Chapter XIII, Title II of the Tax Code of 1997, as implemented by Revenue Regulations No. 2-98, of if they make income payments to individuals or corporations subject to the withholding tax provided for in Section 57 of the Tax Code of 1997, also as implemented by Revenue Regulations No. 2-98.
Source: https://www.bir.gov.ph/images/bir_files/old_files/pdf/3225rmc03_76.pdf
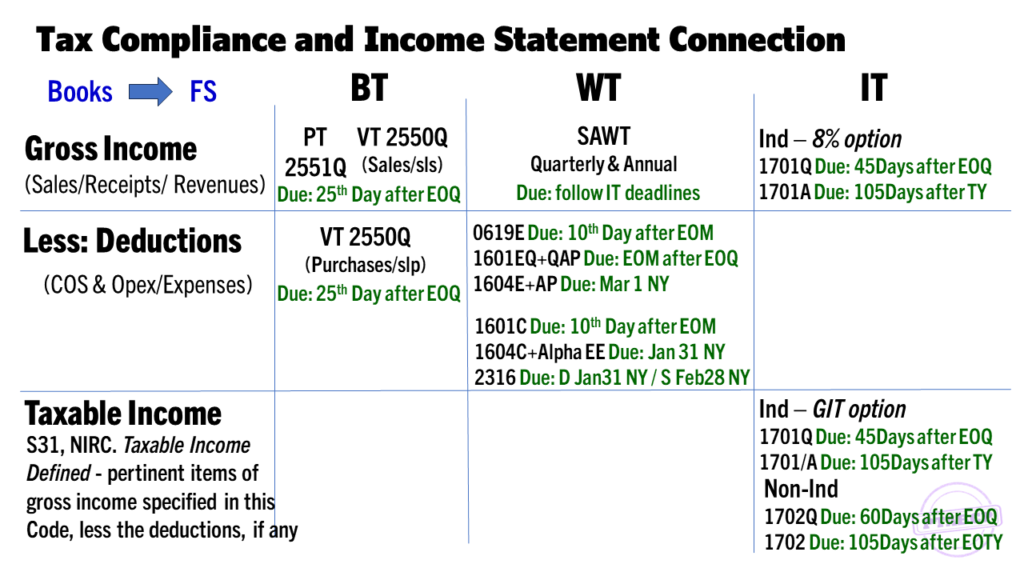
TAXABILITY OF NON-STOCK NON-PROFIT ORGANIZATIONS
Outline:
Part 1 – Taxation of Organization
- Administrative Requirements
- Business Registration Rules
- Books and Records
- Income Tax
- Value-Added Tax
- Percentage Tax
- Withholding Tax
- Sale of Real Property by NSNP
- Charitable Contributions
- Donations to NSNP Organizations
- Sample BIR Ruling on Non-Stock Non-Profit Organization
Part 2 – Tax Exemption
- Application for Tax Exemption and Revalidation
BIR BUSINESS REGISTRATION RULES
SEC. 236. Registration Requirements.[115] -
(A) Requirements. [4]- Every person subject to any internal revenue tax shall register once, either electronically or manually, with the appropriate Revenue District Office:
(1) Within ten (10) days from date of employment, or
(2) On or before the commencement of business,or
(3) Before payment of any tax due, or
(4) Upon filing of a return, statement or declaration as required in this Code.
The registration shall contain the taxpayer's name, place of residence, business and such other information as may be required by the Commissioner in the form prescribed therefor. Provided, That the Commissioner shall ensure the availability of registration facilities to all taxpayers including those who are not residing in the country: Provided, Further, That the Commissioner shall simplify the business registration and tax compliance requirements of self-employed individuals and/or professionals.[205]
A person maintaining a head office, branch or facility shall register with the Revenue District Officer having jurisdiction over the head office, brand or facility. For purposes of this Section, the term 'facility' may include but not be limited to sales outlets, places of production, warehouses or storage places.
Annual Registration Fee - Repealed. [115]
(B) Registration of Each Type of Internal Revenue Tax.- Every person who is required to register with the Bureau of Internal Revenue under Subsection (A) hereof, shall register each type of internal revenue tax for which he is obligated, shall file a return, either electronically or manually, and shall pay, either electronically or manually, such taxes, and shall update such registration of any changes in accordance with Subsection (D) hereof.
(C) Transfer of Registration. - In case a registered person decides to transfer the place of business or head office or branches, it shall be the person's duty to update the registration status by merely filing, either electronically or manually, an application for registration information update in the form prescribed therefor: Provided, however, That if the transferring registered person is subject of an audit investigation, the Revenue District Office which initiated the audit investigation shall continue the same.
(D) Other Updates. - Any person registered in accordance with this Section shall, whenever applicable, update his registration information with the Revenue District Office where he is registered, specifying therein any change in type and other taxpayer details.
(E) Cancellation of Registration. –
(1) General Rule. - The registration of any person shall be cancelled upon mere filing, either electronically or manually, with the Revenue District Office where he is registered an application for registration information update in a form prescribed therefor. However, this shall not preclude the Commissioner of the Internal Revenue or his authorized representative from conducting an audit in order to determine any tax liability;
(2) Cancellation of Value-Added Tax Registration. – A VAT- registered person may cancel the registration for VAT if:
(a) The person makes a written or an electronic application and can demonstrate to the Commissioner’s satisfaction that the gross sales for the following twelve (12) months, other than those that are exempt under Section 109 (A) to (CC), will not exceed the threshold as provided in Section 109 (CC); or
(b) The person has ceased to carry on the trade or business, and does not expect to recommence any trade or business within the next (12) months.
The cancellation of registration will be effective from the first day of the following month.
(F) Persons Required to Register for Value-Added Tax. —
(1) Any person who, in the course of trade or business, sells, barters or exchanges goods or properties, or engages in the sale or exchange of services, shall be liable to register, either electronically or manually, for value-added tax if:
(a) The person's gross sales for the past twelve (12) months, other than those that are exempt under Section 109(A) to (CC),[206] have exceeded the threshold as provided in Section 109(CC); or
(b) There are reasonable grounds to believe that the gross sales for the next twelve (12) months, other than those that are exempt under Section 109(A) to (CC), will exceed the threshold as provided in Section 109 (CC);
(2) Every person who becomes liable to be registered under paragraph (1) of this Subsection shall register, either electronically or manually, with the appropriate Revenue District Office, as determined by the Commissioner. If he fails to register, he shall be liable to pay the tax under Title IV as if he were a VAT-registered person, but without the benefit of input tax credits for the period in which he was not properly registered.
(G) Optional Registration for Value-Added Tax of Exempt Person.
(1) Any person who is not required to register for value-added tax under Subsection (F) hereof may elect to register, either electronically or manually, for value-added tax with the Revenue District Office that has a jurisdiction over the head office of that person.
(2) Any person who elects to register under this Subsection shall not be entitled to cancel his registration under Subsection (E)(2) for the next three (3) years.
Provided, That any person taxed under Section 24(A)(2)(b) and 24(A)(2)(c)(2)(a) of the NIRC who elected to pay the eight percent (8%) tax on gross sales or receipts shall not be allowed to avail of this option.[205]
For purposes of Title IV of this Code, any person who has registered value-added tax as a tax type in accordance with the provisions of Subsection (B) hereof shall be referred to as a “VAT-registered person” who shall be assigned only one Taxpayer Identification Number.
(H) Supplying of Taxpayer Identification Number. –
Any person required under the authority of this Code to make, render or file a return, statement or other document shall be supplied with or assigned a Taxpayer Identification Number which the person shall indicate in such return, statement or document filed, either electronically or manually, with the Bureau of Internal Revenue for his proper identification for tax purposes, and which the person shall indicate in certain documents, such as, but not limited to the following:
(1) Sugar quedans, refined sugar release order or similar instruments;
(2) Domestic bills of lading;
(3) Documents to be registered with the Register of Deeds or Assessor's Office;
(4) Registration certificate of transportation equipment by land, sea or air;
(5) Documents to be registered with the Securities and Exchange Commission;
(6) Building construction permits;
(7) Application for loan with banks, financial institutions, or other financial intermediaries;
(8) Application for mayor's permit;
(9) Application for business license with the Department of Trade & Industry; and
(10) Such other documents which may hereafter be required under rules and regulations to be promulgated by the Secretary of Finance, upon recommendation of the Commissioner.
In cases where a registered taxpayer dies, the administrator or executor shall register, either electronically or manually, the estate of the decedent in accordance with Subsection (A) hereof and a new Taxpayer Identification Number shall be supplied in accordance with the provisions of this Section.
In the case of a nonresident decedent, the executor or administrator of the estate shall register, either electronically or manually, the estate with the Revenue District Office where the executor or administrator is registered: Provided, however, That in case such executor or administrator is not registered, registration of the estate shall be made with the Taxpayer Identification Number supplied by the Revenue District Office having jurisdiction over the executor or administrator's legal residence.
Only one Taxpayer Identification Number shall be assigned to a taxpayer. Any person who shall secure more than one Taxpayer Identification Number shall be criminally liable under the provision of Section 275 on “Violation of Other Provisions of this Code or Regulations in General”.
Source: https://www.bir.gov.ph/index.php/tax-code.html#title9
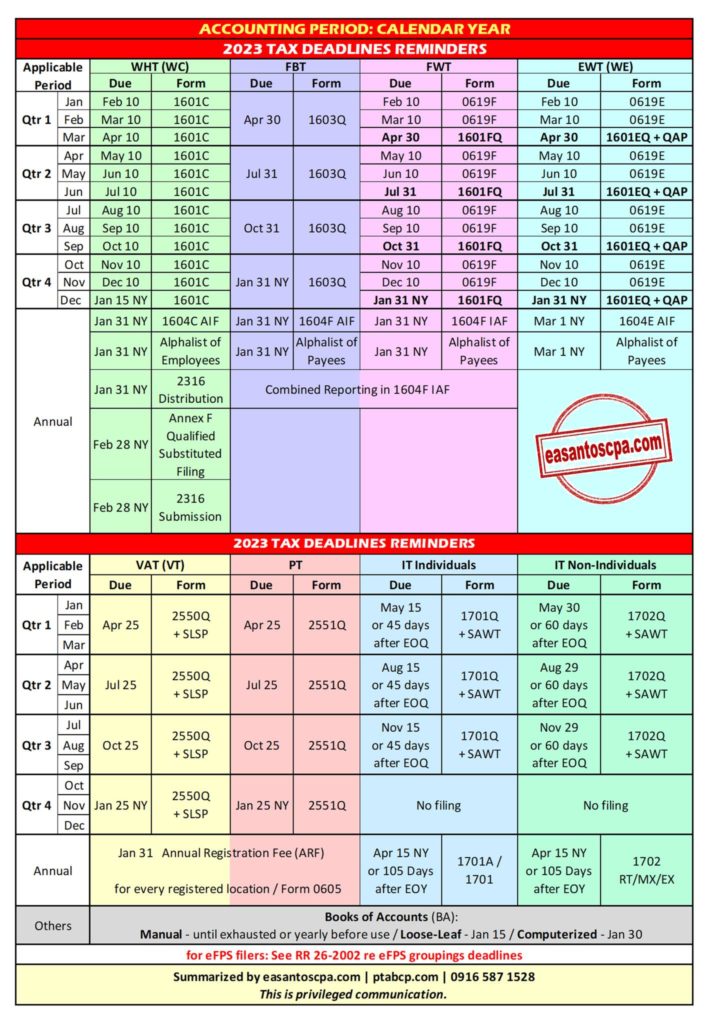
SECTION 6. Prescribed Periods to Complete Primary Registration. - Every person subject to any internal revenue tax to be filed/paid periodically shall complete its registration with the BIR as follows:
On or before the commencement of business. - Self-employed individuals, estates and trusts, corporations and their branches, if any.
Source: Revenue Regulations No. 7-2012
"Commencement of Business" - in the case of pursuit of business or practice of profession, it shall be reckoned from the day when the first sale transaction occurred or within thirty (30) calendar days from the issuance of Mayor's Permit / Professional Tax Receipt (PTR) by LGU, or Certificate or Registration issued by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), whichever comes earlier.
Source:
Revenue Regulations No. 7-2012
RR 7-2012 Annex A List of Documentary Requirements
Updated List of Requirements - Refer to BIR Citizens Charter
- Issued to individuals engaged in business or practice of profession and to juridical persons (whether) taxable or exempt) by the BIR district office concerned (i.e. BIR district office of HO/Branch/Facility) upon compliance with the requirements for registration.
Source: Revenue Regulations No. 7-2012
Persons required to apply for COR shall post or exhibit his/its original COR and duly validated Annual Registration Fee Return at his/its principal place of business and at each branch and/or facility in a way that is clearly and easily visible to the public.
Source: Revenue Regulations No. 7-2012
Note: RA 11976 EOPT Law deletes the provision for Annual Registration Fee effective January 22, 2024.
Annual Registration Fee is Repealed by RA 11976 Ease of Paying Taxes (EOPT) Law.
Source: https://www.officialgazette.gov.ph/downloads/2024/01jan/20240105-RA-11976-FRM.pdf
Every person, who is required to register with the BIR under Section 4 of these Regulations, shall register each type of internal revenue tax for which he/it is obligated to file a return or pay taxes due thereon. Such person shall update the BIR for any changes in his/its registration information in accordance with Section 11 hereof.
Source: Revenue Regulations No. 7-2012
Note: RA 11976 EOPT Law deletes the provision for Annual Registration Fee effective January 22, 2024.
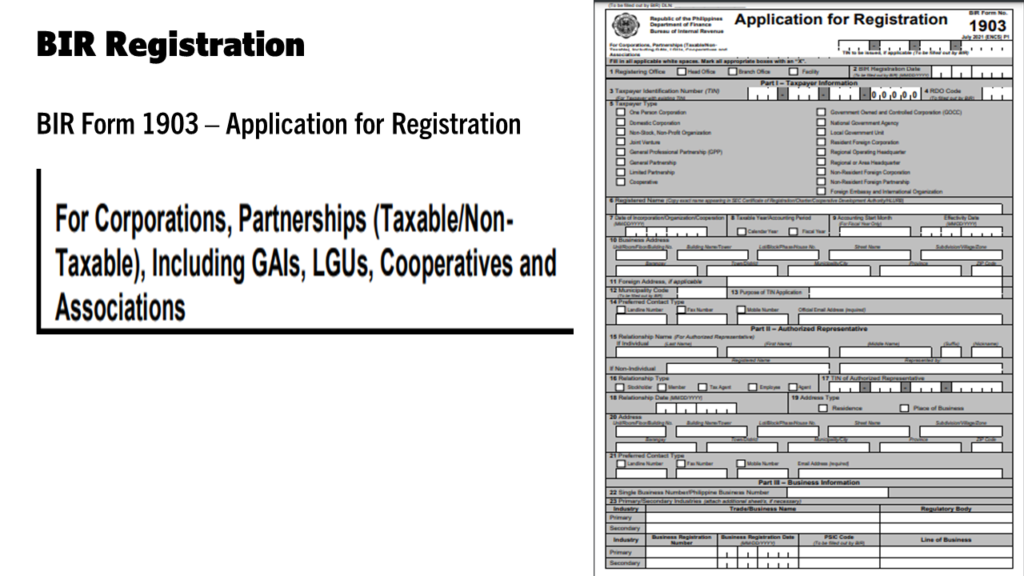
Any entity must register their business or practice of profession with the Bureau of Internal Revenue (BIR)
BIR Registration for Non-Individual
- Accomplish BIR Form 1903
- Attach Documentary Requirements

BOOKS AND RECORDS
New business registrant may proceed to registration of books of accounts after securing COR and ATP within thirty (30) calendar days from the date of business registration with the Bureau.
Source: RMC No. 30-2018 Amends documentary requirements for new business registrants
Register and Keep Books of Accounts
The National Internal Revenue Code (NIRC) mandates that a Taxpayer (TP) shall keep Books Of Accounts.
Keeping of Books of Accounts
Legal Basis:
Sec.232 (A), NIRC, as amended. Corporations, Companies, Partnerships or Persons Required to Keep Books of Accounts. - All corporations, companies, partnerships or persons required by law to pay internal revenue taxes shall keep and use relevant and appropriate set of bookkeeping records duly authorized by the Secretary of Finance wherein all transactions and results of operations are shown and from which all taxes due the Government may readily and accurately be ascertained and determined any time of the year.
Provided, that corporations, companies, partnerships or persons whose gross annual sales, earnings, receipts or output exceed Three Million pesos (P3,000,000), shall have their books of accounts audited and examined yearly by independent Certified Public Accountants and their income tax returns accompanied with a duly accomplished Account Information Form(AIF) which shall contain, among others, information lifted from certified balance sheets, profit and loss statements, schedules listing income-producing properties and the corresponding income therefrom and other relevant statements
Thus, a Taxpayer shall apply and register for Books Of Accounts (BOA) with the Bureau of Internal Revenue (BIR), the only body which has authority over Books Of Accounts
===
What Books Of Accounts must be registered with the BIR?
TAX EXEMPTION AND REVALIDATION
Revenue Memorandum Order No. 20-2013
SECTION 2. Application for Tax Exemption and Revalidation
Corporations and associations enumerated under Section 30 of the NIRC, as amended, including those which have been issued tax exemption rulings/certificates prior to June 30, 2012 shall file their respective Applications for Tax Exemptions/Revalidation with the Revenue District Office (RDO) where they are registered. Only corporations or associations that are duly qualified under Section 30 of the NIRC, as amended, shall be issued Tax Exemption Rulings.
Source: RMO 20-2013 Issuance of Tax Exemptions Rulings to Qualified NSNP
Revenue Memorandum Order No. 20-2013
Validity of the Tax Exemption Ruling. - A Tax Exemption Ruling issued under this Order shall be valid for a period of three (3) years from the date of effectivity specified in the Ruling, unless sooner revoked or cancelled.
Source: RMO 20-2013 Issuance of Tax Exemptions Rulings to Qualified NSNP
II. Effects of Non-filing, late filing and/or revocation of Tax Exemption Rulings
Source: RMO 34-2014 Clarifications on the Issuance of Tax Exemption Rulings
INCOME TAX
INCOME TAX RATES FOR NON-INDIVIDUALS



BIR Form 1702-EX
VALUE-ADDED TAX
Business Tax comes in two forms:
- Percentage Tax, or
- Value Added Tax
PERCENTAGE TAX
Business Tax comes in two forms:
- Percentage Tax, or
- Value Added Tax
WITHHOLDING TAX
Withholding Taxes - Sec.58(A), NIRC
- A manner or system of collecting taxes with the end in view of collecting in advance the full amount of tax or at least the approximate tax due from the payee on certain income payments
- The amount withheld is a special trust fund in trust for the government until paid or remitted by WA to BIR
SALE OF REAL PROPERTY BY NSNP
Moreover, Section 30 of Revenue Regulations No. 2, as amended, provides, among others, that the income of such tax-exempt corporation which is considered as income from its properties, real or personal, includes profits from the sale of property. In other words, the sale by MIDFI of its real property shall be subject to the corresponding income tax imposed under the Tax Code of 1997.
Such being the case, this Office hereby rules that the sale by Mary immaculate Development Foundation, Inc. (MIDFI) of its real property is subject to capital gains tax based on the selling price or current fair market as determined in accordance with Section 6 (E) of the Tax Code of 1997, whichever is higher, of such land and/or buildings pursuant to Section 27 (D) (5) of the same Code (Section 4 (c) (i), Revenue Regulations No. 7-2003). Moreover, the Deed of Absolute Sale of said real property shall be subject to documentary stamp tax imposed under Section 196 of the Tax Code of 1997.
Source: BIR Ruling 023-10
CHARITABLE CONTRIBUTIONS
DONATIONS TO NSNP ORGANIZATIONS
Accommodation Service Business can be operated by Individual or Non-Individual Entities. Being so, they must register their accommodation service business with the Bureau of Internal Revenue (BIR)

BIR Registration for Individual
- Accomplish BIR Form 1901
- Attach Documentary Requirements


BIR Registration for Non-Individual
- Accomplish BIR Form 1903
- Attach Documentary Requirements


SAMPLE BIR RULING ON NON-STOCK NON-PROFIT ORGANIZATION
Accommodation Service Business can be operated by Individual or Non-Individual Entities. Being so, they must register their accommodation service business with the Bureau of Internal Revenue (BIR)

BIR Registration for Individual
- Accomplish BIR Form 1901
- Attach Documentary Requirements


BIR Registration for Non-Individual
- Accomplish BIR Form 1903
- Attach Documentary Requirements


Register and Keep Books of Accounts
The National Internal Revenue Code (NIRC) mandates that a Taxpayer (TP) shall keep Books Of Accounts.
Keeping of Books of Accounts
Legal Basis:
Sec.232 (A), NIRC, as amended. Corporations, Companies, Partnerships or Persons Required to Keep Books of Accounts. - All corporations, companies, partnerships or persons required by law to pay internal revenue taxes shall keep and use relevant and appropriate set of bookkeeping records duly authorized by the Secretary of Finance wherein all transactions and results of operations are shown and from which all taxes due the Government may readily and accurately be ascertained and determined any time of the year.
Provided, that corporations, companies, partnerships or persons whose gross annual sales, earnings, receipts or output exceed Three Million pesos (P3,000,000), shall have their books of accounts audited and examined yearly by independent Certified Public Accountants and their income tax returns accompanied with a duly accomplished Account Information Form(AIF) which shall contain, among others, information lifted from certified balance sheets, profit and loss statements, schedules listing income-producing properties and the corresponding income therefrom and other relevant statements
Thus, a Taxpayer shall apply and register for Books Of Accounts (BOA) with the Bureau of Internal Revenue (BIR), the only body which has authority over Books Of Accounts
===
What Books Of Accounts must be registered with the BIR?
Gross Receipts
Per Sec. 2 (g), RR 8-2018; Jan 25, 2018
Refers to the total amount of money or its equivalent representing contract price, compensation, service fee, rental or royalty, including the amount charged for materials supplied with the services, and deposits and advance payments actually or constructively received during the taxable period for the services performed or to be performed for another person, except returnable security deposits for purposes of these regulations.
In the case of VAT taxpayer, this shall exclude the VAT component
Gross Receipts - Hotel, motel, rest/pension/lodging house and resort operators
Republic Act No. 11360
AN ACT PROVIDING THAT SERVICE CHARGES COLLECTED BY HOTELS, RESTAURANTS AND OTHER SIMILAR ESTABLISHMENTS BE DISTRIBUTED IN FULL TO ALL COVERED EMPLOYEES, AMENDING FOR THE PURPOSE PRESIDENTIAL DECREE NO. 442, AS AMENDED, OTHERWISE KNOW AS THE “LABOR CODE OF THE PHILIPPINES”
Art. 96. Service Charges. – All service charges collected by hotels, restaurants, and similar establishments shall be distributed completely and equally among the covered workers except managerial employees.
In the event that the minimum wage is increased by law or wage order, service charges paid to the covered employees shall not be considered in determining the employer’s compliance with the increased minimum wage.
Supreme Court (SC) decision regarding deductions
When a taxpayer claims a deduction, he must point to some specific provision of the statute in which that deduction is authorized and must be able to prove that he is entitled to the deduction which the law allows. An item of expenditure, therefore, must fall squarely within the language of the law in order to be deductible.
Cost of Service
Business Tax comes in two forms:
- Percentage Tax, or
- Value Added Tax
Withholding Taxes - Sec.58(A), NIRC
- A manner or system of collecting taxes with the end in view of collecting in advance the full amount of tax or at least the approximate tax due from the payee on certain income payments
- The amount withheld is a special trust fund in trust for the government until paid or remitted by WA to BIR
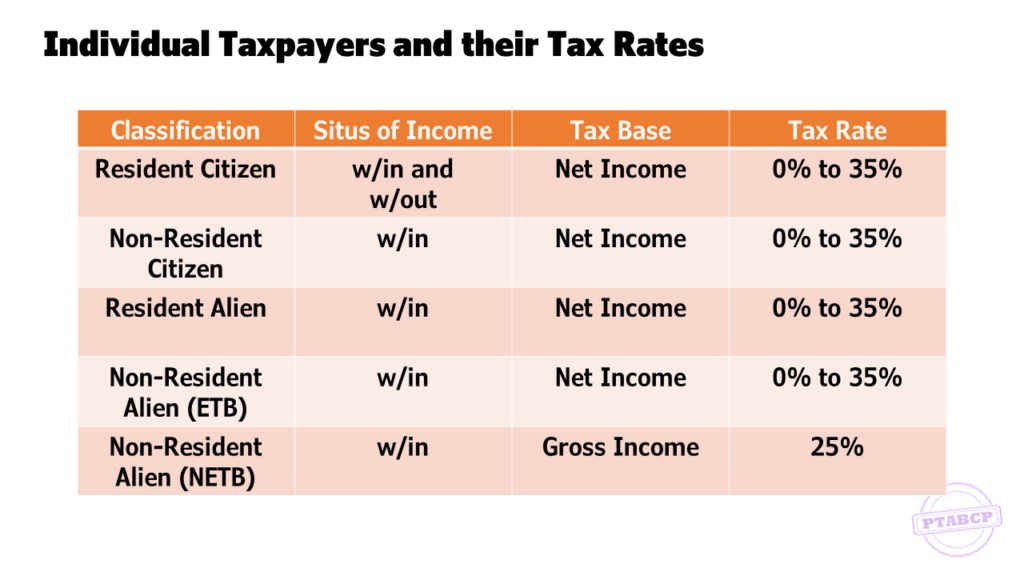
INCOME TAX RATES FOR INDIVIDUALS
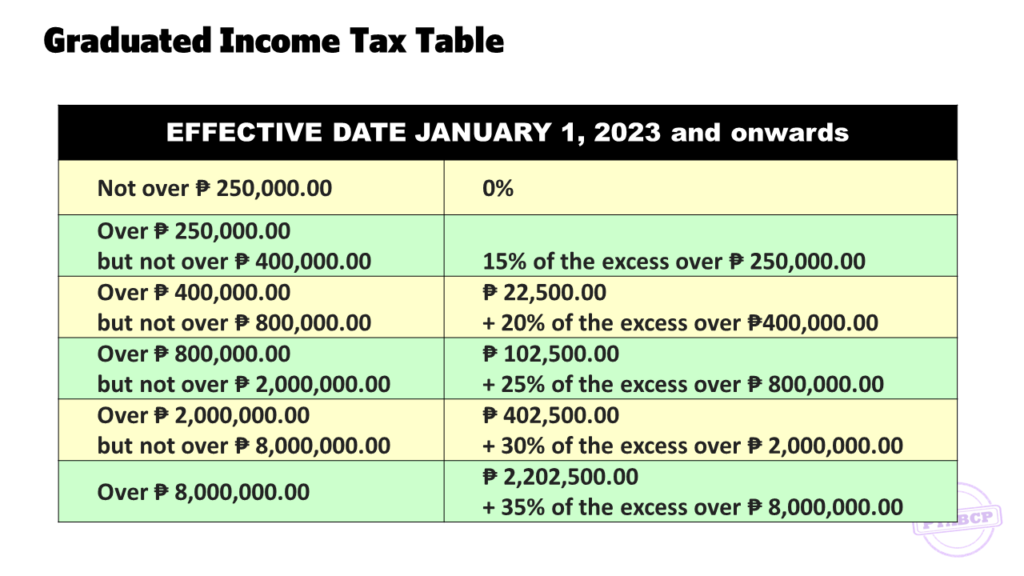
INCOME TAX RATES FOR NON-INDIVIDUALS



SEC COMPLIANCE – ATTACHMENTS TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The following documents shall be filed with the annual financial statements and in the interim financial statements, if required herein:
Business Tax comes in two forms:
- Percentage Tax, or
- Value Added Tax